Our Health Library information does not replace the advice of a doctor. Please be advised that this information is made available to assist our patients to learn more about their health. Our providers may not see and/or treat all topics found herein.
Barium Enema
Test Overview
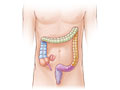
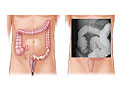
A barium enema is an X-ray exam of the large intestine (colon and rectum). It may also be called a lower gastrointestinal (GI) exam. The test is used to help find diseases and other problems that affect the large intestine. The colon is filled with a contrast material that contains barium so that the intestine can be seen on an X-ray. This is done by pouring the contrast material through a tube inserted into the anus. The barium blocks X-rays. This causes the barium-filled colon to show up clearly on the X-ray picture.
There are two types of barium enemas.
- In a single-contrast study, the colon is filled with barium. This outlines the intestine and shows large abnormalities.
- In a double-contrast or air-contrast study, the colon is first filled with barium, and then the barium is drained out. This leaves only a thin layer of barium on the wall of the colon. The colon is then filled with air. This provides a detailed view of the inner surface of the colon. It makes it easier to see narrowed areas (strictures), diverticula, and swelling.
The single-contrast study may be the better choice for certain medical reasons. It may also be a good choice for older people who may not be able to tolerate a double-contrast study, which takes longer and is more uncomfortable. If the results are not clear, then a double-contrast study may also be done.
Why It Is Done
A barium enema is done to:
- Find swelling of the intestinal wall that occurs in inflammatory bowel diseases. Examples are ulcerative colitis and Crohn's disease. A barium enema also may be used to keep track of the progress of these diseases.
- Find problems with the structure of the large intestine. Problems may include narrowed areas (strictures) or pockets or sacs (diverticula) in the intestinal wall.
- Help correct a condition called ileocolic intussusception. This occurs when the end of a child's small intestine protrudes into the large intestine.
- Check on belly symptoms such as pain, blood in stool, or altered bowel habits.
- Check on other problems such as anemia or unexplained weight loss.
How To Prepare
- For 1 to 3 days before the test, you will drink water, fruit juices, plain coffee or tea, and broth.
- On the day before the test:
- Drink plenty of fluids. If you have kidney, heart, or liver disease and have to limit fluids, talk with your doctor before you increase the amount of fluids you drink.
- You will take a laxative. Your doctor will give you this to empty your intestines.
- You may be asked to do a water enema to clean your colon. You may need to do this again on the day of the test.
Before a barium enema, tell your doctor if you:
- Are or think you may be pregnant.
- Are allergic to latex. Latex products are often used to give the barium. If you are allergic to latex, different products will be used.
- Are allergic to barium.
- Have had an upper digestive barium test (upper GI or barium swallow) recently.
After the test, you may have light-colored stools and cramping for a few days.
How It Is Done
During the test
The colon is filled with a contrast material that contains barium so that the colon can be seen on an X-ray. This is done by pouring the contrast material through a tube inserted into the anus. The barium blocks X-rays, causing the barium-filled colon to show up clearly on the X-ray picture.
- You will lie on the X-ray table while the first X-ray film is taken.
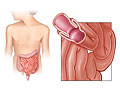
- While you are lying on your side, a well-lubricated enema tube will be inserted gently into your rectum. The barium contrast material is then allowed to flow slowly into your colon.
- A small balloon on the enema tip may be filled with air to help you hold in the barium. Tightening your anal sphincter muscle (as if you were trying to hold back a bowel movement) against the tube may help. Taking slow, deep breaths may also help.
- You may be given a shot of medicine to relieve the cramping.
Your doctor will watch the flow of the barium through your colon on an X-ray fluoroscope monitor that is like a TV screen.
- You will be asked to turn to different positions (sides, front, and back). The table may be tilted slightly to help the barium flow through your colon and to take X-rays from different directions.
- Your doctor may also press gently on your belly with his or her hand or a plastic paddle. This can help move the barium through your intestines.
- If a double-contrast study is being done, the barium will be drained out and your colon will be filled with air.
A single-contrast study usually takes 30 to 45 minutes. But the actual time the barium is held inside is only 10 to 15 minutes. A double- or air-contrast study may take up to an hour.
After the test
When the test is finished:
- The enema tube is removed.
- You will be given a bedpan or be taken to the toilet to get rid of as much of the barium as you can.
- One or two more X-ray pictures (post-evacuation films) will then be taken.
After the test, you may go back to your regular diet unless your doctor gives you other instructions. Be sure to drink plenty of liquids. They replace those you have lost, and they help flush the remaining barium out of your system. Your bowel movements may look white or pinkish for 1 to 2 days after the test. Your doctor may tell you to take a medicine, such as a laxative, to help you pass the rest of the barium.
How It Feels
A barium enema can be uncomfortable and tiring. But it usually doesn't last very long.
Many people report that the preparation and bowel cleaning are the hardest parts. The laxative may not taste good, and the frequent bowel movements can be tiring. Also, the anal area can become quite sore during the process. Warm sitz baths or a local anesthetic salve, such as Preparation H, can help ease this discomfort.
You may be embarrassed by the test. You may worry that you won't be able to hold the barium and that it will leak onto you or onto the table. The doctors who perform this procedure are used to this. They will be able to help you.
The X-ray table is hard and sometimes cold because air-conditioning is used to keep the equipment cool. When the barium first flows into your colon, it may feel a bit cool. As your colon fills, you may have a feeling of fullness, moderate cramping, and a strong urge to have a bowel movement. If an air-contrast study is performed, you may feel more cramping or gas pains from having gas pumped into your large intestine. Taking slow, deep breaths through your mouth can help you relax.
The test may take awhile. You may want to bring something to do quietly (like bringing a book or magazine to read).
You may feel tired for a day or so after the test. Make sure to arrange for someone to drive you home after the test. This test can be exhausting.
Risks
There is very little chance of a problem from having a barium enema.
- Sometimes the barium that remains in the colon hardens. This can cause severe constipation (impaction) or obstruction. To decrease your risk, drink extra fluids after the test. If your doctor recommends it, use an enema or mild laxative after the test.
- In rare cases, barium can cause swollen areas in the colon. These are called barium granulomas.
- Perforation of the bowel is a more serious, but very rare, complication. Under the pressure from the barium or air, a weakened section of the colon may break open. This allows the contents of the intestine to spill into the abdominal cavity. It may occur in people whose bowel wall has been weakened by intestinal problems, such as inflammatory bowel diseases (ulcerative colitis or Crohn's disease).
Results
The results of a barium enema are usually ready right after the test or within a few days.
Normal: | The colon looks normal. |
|---|---|
Abnormal: | One or more problems in the colon are found, such as:
|
Many conditions can change barium enema test results. Your doctor will discuss any important abnormal results with you in relation to your symptoms and past health.
Related Information
Credits
Current as of: July 31, 2024
Author: Ignite Healthwise, LLC Staff
Clinical Review Board
All Healthwise education is reviewed by a team that includes physicians, nurses, advanced practitioners, registered dieticians, and other healthcare professionals.
Current as of: July 31, 2024
Author: Ignite Healthwise, LLC Staff
Clinical Review Board
All Healthwise education is reviewed by a team that includes physicians, nurses, advanced practitioners, registered dieticians, and other healthcare professionals.
This information does not replace the advice of a doctor. Ignite Healthwise, LLC disclaims any warranty or liability for your use of this information. Your use of this information means that you agree to the Terms of Use and Privacy Policy. Learn how we develop our content.
To learn more about Ignite Healthwise, LLC, visit webmdignite.com.
© 2024-2025 Ignite Healthwise, LLC.